- Inicio
- Inteli Consulting
- Planeación Estratégica
- Servicios Marketinginteli
- Fundamentos de Publicidad
- Branding
- Entorno de Marketing
- Fundamentos de Marketing
- Estrategias de Producto
- Canales de Distribución
- Análisis de la competencia
- Estrategias de precio
- Casos Empresariales
- Caso Bimbo
- Caso Barcelona Fútbol Club
- Caso Tesla
- Caso BBC
- Caso Starbucks
- Caso Adidas
- Caso Disney
- Caso Femsa
- Caso Juan Valdez
- Caso Alpina
- Caso D1
- Caso Zara
- Caso Netflix
- Caso IKEA
- Caso Industrias Haceb
- Caso Andrés Carne de Res
- Caso AIRBNB
- Cinco casos de éxito de experiencias de marca
- Casos Marketing
- Caso Totto
- Caso Bon Bon Bum
- Caso Nike Jordan
- Caso Crepes&Waffles
- Caso Ramo
- Caso Chocolatina JET
- Caso Quala
- Caso Crem Helado
- Caso Marketing digital Pastelería Doña Julia
- Caso Lego
- Caso Tostao
- Caso Cerveza Corona
- Caso Nutella
- Caso Moco de Gorila
- Caso Cerveza Artesanal
- Caso Café Especial Andes Ecocafé
- Caso bebida natural
- Casos Comercio electrónico
- Gerencia de Ventas
- Marketing Internacional
- Sistema de Informacion de Marketing
- Investigacion de Mercados
- Comportamiento del consumidor
- Las percepciones
- Marketing Insights
- Investigación Publicitaria
- Teorías de aprendizaje
- Comportamiento del consumidor y la tecnología
- Comportamiento del consumidor y las necesidades
- Perfil del consumidor
- Conocimiento del cliente
- Comportamiento del consumidor en épocas de crisis
- Perfil psicográfico del consumidorr
- Marketing de Experiencias
- Marketing de Engagement
- Elementos claves en el comportamiento del consumidor
- Gerencia de Servicio
- Marketing de contenidos
- Estrategias de comunicación en marketing
- Marketing Digital
- Conceptos básicos de marketing digital
- Diagnóstico de Madurez Digital
- ¿Qué Necesita Mi Marca en el Mundo Digital?
- Sistemas ERP para soluciones de marketing
- Tipos de presencia on-line
- Sistemas ERP para soluciones de marketing
- Generación de Tráfico
- Inbound Marketing
- Métricas del Marketing Digital
- Disrupción Digital
- SEO
- Tendencias actuales en Data Science
- SEM
- Marketing en redes sociales
- Descarga videos Youtube
- E-mail Marketing
- Tipos Hosting
- Comercio Electrónico
- Marketing segmentos
- Contacto
Basic Marketing Concepts

¿What does marketing mean?
Marketing consists of all the activities of individuals and organizations designed to identify, anticipate, and mutually satisfy the needs of all parties involved in the exchange.
Lets talk about your Digital marketing strategy
The total of activities involved in the transfer of goods or services from the producer or seller to the consumer or buyer, including advertising, shipping, storing, and selling.
Marketing is typically seen as the task of creating, promoting and delivering differentiated goods and services to consumers and businesses at a profit.
What can we market
- Places
- Properties
- Organizations
- Goods
- Services
- Experiences
- Information
- Ideas
- Events
- Persons
Marketing Mix

What are the 4 P’s?
- Product / Value proposition / Consumer wants and needs.
- Price / Cost to satisfy
- Place/ Distribution channels
- Promotion/ communications / advertising
Product: This variable described all factors relating to the actual product visible to the consumer. These may include things such as quality, features, options, style, packaging, brand, sizes, labels, variety, and warranties.
Price: The price variable includes not only the list price, but all other pricing factors associated with a product. These may include discounts, allowances, payment options and periods, and credit terms. All of these are related to the final, whole price of the product.
Place: Place deals with all distribution and location aspects of a product. How and what are the products available to consumers? These may include assortments, channels, coverage areas, locations, and inventories.
Promotion: Promotion is any and all efforts by a company to make publicize a product and make the consumer aware of it. Efforts might include advertising, personal selling, sales, public relations, or internet activities.
Segmentation and targeting
Market Segmentation: Market segmentation is the act of subdividing the market into a group or groups of people who have similar needs within the group, but dissimilar needs across the groups. An example would be people wanting cars, but different types of cars. The different types of cars may be luxury, sports , or SUV's.
Targeting: The marketing mix should only be determined after a target market is determined.
Target market: The group or groups of customers for which the marketer will direct attention. This group is determined after thorough segmentation and analysis of the market.
Marketing Positioning
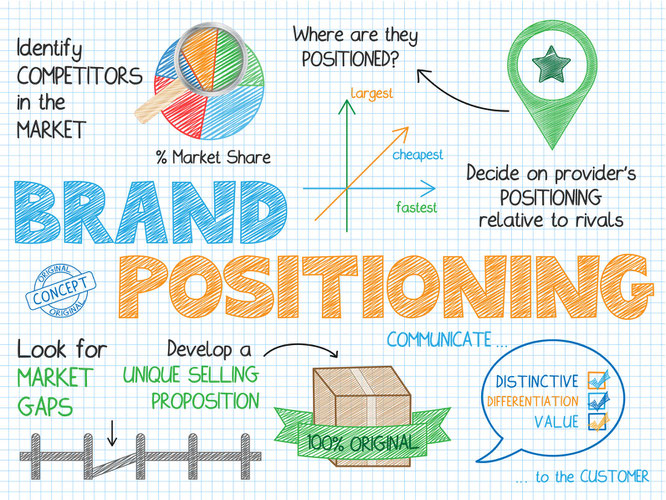
In marketing and business strategy, market position refers to the consumer's perception of a brand or product in relation to competing brands or products. Market positioning refers to the process of establishing the image or identity of a brand or product so that consumers perceive it in a certain way.
There are several types of positioning strategies. A few examples are positioning by:
- Product attributes and benefits: Associating your brand/product with certain characteristics or with certain beneficial value
- Product price: Associating your brand/product with competitive pricing
- Product quality: Associating your brand/product with high quality
- Product use and application: Associating your brand/product with a specific use
- Competitors: Making consumers think that your brand/product is better than your competitors
Brand Equity

Brand equity is a marketing term that describes a brand’s value. That value is determined by consumer perception of and experiences with the brand. If people think highly of a brand, it has positive brand equity. When a brand consistently under delivers and disappoints to the point where people recommend that others avoid it, it has negative brand equity. Brand equity refers to a value premium that a company generates from a product with a recognizable name when compared to a generic equivalent. Companies can create brand equity for their products by making them memorable, easily recognizable, and superior in quality and reliability.
Positive brand equity has value:
Companies can charge more for a product with a great deal of brand equity.
That equity can be transferred to line extensions – products related to the brand that include the brand name – so a business can make more money from the brand. It can help boost a company’s stock price.
Brand equity develops and grows as a result of a customer’s experiences with the brand. The process typically involves that customer or consumer’s natural relationship with the brand that unfolds following a predictable model:
Awareness: The brand is introduced to its target audience – often with advertising – in a way that gets it noticed.
Recognition: Customers become familiar with the brand and recognize it in a store or elsewhere.
Trial: Now that they recognize the brand and know what it is or stands for, they try it.
Preference: When the consumer has a good experience with the brand, it becomes the preferred choice.
Loyalty: After a series of good brand experiences, users not only recommend it to others, it becomes the only one they will buy and use in that category. They think so highly of it that any product associated with the brand benefits from its positive glow.
External factors, macro environment
Demographic environment: The features of a country that can be statistically described
Economic environment: The financial and economic conditions in a country will determine demand for any and all products.
Competitive environment: The intensity of competition in the market the business is in cannot be controlled.
Physical environment : Availability, use, and disposal of natural resources.
Technological environment: Determines how the marketing should be done. What medium should be used?
Political and legal environment: Laws and restrictions may be set by various government agencies in regard to competition, consumer protection, or societal welfare.
Social/Cultural environment: What is acceptable in what culture may not be acceptable in another.
Company related environment - Goals and objectives of the company as a whole.
Digital Marketing

Digital marketing encompasses all marketing efforts that use an electronic device or the internet. Businesses leverage digital channels such as search engines, social media, email, and their websites to connect with current and prospective customers. Digital marketing, the promotion of products or brands via one or more forms of electronic media, differs from traditional marketing in that it uses multiple channels and methods that enable an organization to analyze marketing campaigns and understand what is working and what isn’t – typically in real time.
Marketing Trends
1) Artificial Intelligence
2) Programmatic Advertising: Programmatic advertising means using AI to automate ad buying so you can target more specific audiences
3) Chatbots
4) Personalization: If you want to stand out in 2019, you need to personalize your marketing – and that means personalized content, products, emails, and more.
5) Video Marketing
6) Influencer Marketing
